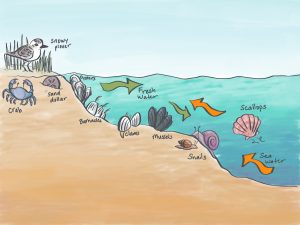
a pebbly or sandy shore, especially by the ocean between high- and low-water marks

by ldwhite3
a pebbly or sandy shore, especially by the ocean between high- and low-water marks

by ldwhite3
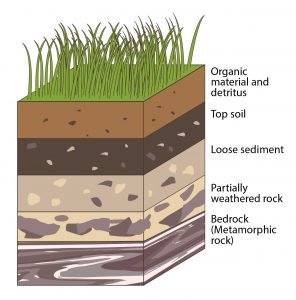
A diagram of an environmental or geological setting in the shape of a three-dimensional box, containing cross-sections along two vertical sides and the top of the box
by ldwhite3
Erosion of rock, shells, wood, and other hard surfaces by organisms. Examples include bivalves that create holes in rock and wood, parrotfish that erode coral while grazing on algae, barnacles that attach to bivalve shells, and sponges that bore small holes into bivalve shells.

by ldwhite3
Solid (or nearly solid) rock exposed at the surface or underlying surface sediment (including soil).
by ldwhite3
A marine invertebrate belonging to the Cirripedia in the Crustacea, which is a part of the Phylum Arthropoda (thus related to crabs and lobsters), and characterized by a hard shell attached to a hard surface. Barnacles are filter-feeders, resembling shrimps living upside down in a box. It is sometimes possible to find fossil barnacles whole, often still attached to other shells.

by eclites
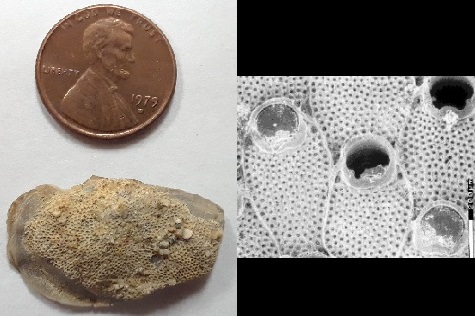
A marine or freshwater, colonial invertebrate belonging to the Phylum Bryozoa; many are characterized by branching mineralized exoskeletons from which multiple individuals (zooids) extend from small pores to filter feed using crowns of tentacles (lophophores). Bryozoans have a long and exemplary fossil record and are especially common in Paleozoic (540 to 250 million year old) rocks. One of the more common Paleozoic varieties looks like fine-mesh cloth with numerous tiny holes in which the individual animals in the colony lived (see image on the left). Although they function somewhat like coral, and are often found in similar environments, bryozoans are more closely related to brachiopods. Image on right side shows what bryozoans look like up at high magnification, under a scanning electron microscope.
by eclites
A marine or freshwater invertebrate belonging to the Class Bivalvia in the Phylum Mollusca. Bivalves are generally called “clams,” but they also include scallops, mussels, cockles, and oysters. Bivalves are characterized by right and left shells. Each half of these hinged shells is called a valve. Bivalves are filter feeders, collecting food particles from the water with their gills.

by troque
The number of kinds of organisms at any given time and place. Global changes in biodiversity through geologic time tell paleontologists that something is happening to the rate of extinction or the rate of origination of new species. Regional changes in biodiversity are influenced by migration, or the number of species supported by available food and space resources.